
Cancer screening plays a crucial role in early detection, enabling timely interventions and improving survival rates. With advancements in technology, cancer screening in Singapore offers various methods tailored to different types of cancers and individual needs. Understanding the options and choosing the right test is essential for effective prevention and management.
What Is Cancer Screening?
Cancer screening involves tests and examinations designed to detect cancer in its early stages, often before symptoms appear. The purpose is to identify abnormalities that may indicate cancer or its precursors, allowing for early treatment. Early detection significantly improves treatment success rates and reduces complications.
How Cancer Screening Works
Screening tests work by identifying abnormal cells or changes in the body that could indicate the presence of cancer. Different screenings are tailored to specific cancers, such as breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancer. These tests range from imaging scans and blood tests to biopsies and molecular screenings. Regular screenings as recommended by healthcare professionals can help monitor changes over time and spot early signs.
Why Is Cancer Screening Important?
Cancer often develops silently, with no noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Screening can detect potential issues before they become serious. Early intervention through cancer screening in Singapore not only enhances the chances of successful treatment but also reduces the financial and emotional burden on patients and families. It is a proactive measure to safeguard one’s health.
Types of Cancer Screening Tests
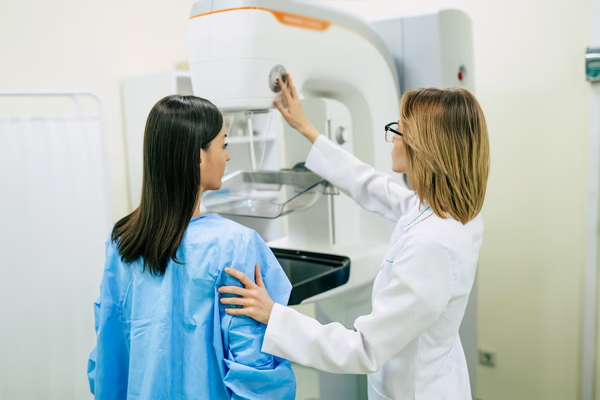
Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening is primarily done through mammograms, which use low-dose X-rays to detect changes in breast tissue. Women aged 40 and above are generally recommended to undergo regular mammograms, although the frequency may vary based on individual risk factors.
Cervical Cancer Screening
Pap smears and HPV tests are common for detecting cervical cancer. Pap smears identify precancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix, while HPV tests screen for the virus that can cause cervical cancer. Women aged 25 to 65 should consider regular cervical screening every three to five years.
Colorectal Cancer Screening
Colorectal cancer screening includes methods like fecal immunochemical tests (FIT), colonoscopies, and sigmoidoscopies. FIT detects hidden blood in the stool, while colonoscopies and sigmoidoscopies allow doctors to examine the colon for polyps or abnormal growths.
Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer is typically screened using the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, which measures PSA levels in the blood. High levels may indicate prostate cancer or other prostate-related conditions. Digital rectal exams (DRE) are sometimes used in conjunction with PSA testing for comprehensive assessment.
Lung Cancer Screening
Lung cancer screening is conducted through low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans, especially for individuals with a history of heavy smoking. LDCT scans create detailed images of the lungs, making it easier to detect abnormalities.
Skin Cancer Screening
Skin cancer screening involves visual examinations by dermatologists. Suspicious moles or skin lesions may be biopsied for further analysis. Regular self-checks and dermatological assessments are recommended for individuals with high sun exposure or a family history of skin cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Screening
Screening for ovarian cancer includes transvaginal ultrasounds (TVUS) and CA-125 blood tests. TVUS examines the ovaries and uterus, while CA-125 measures protein levels that may be elevated in ovarian cancer cases.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cancer Screening Test
Age and Gender
Certain screenings, such as mammograms and Pap smears, are specific to age groups and genders. It’s essential to follow age-appropriate guidelines to ensure effective detection.
Personal and Family Medical History
A family history of cancer may increase the risk of developing specific types of cancer. Screening recommendations are often tailored to individual medical backgrounds.
Lifestyle and Habits
Lifestyle factors such as smoking, diet, and physical activity influence cancer risk. Smokers, for instance, may require lung cancer screening earlier than non-smokers.
Risk Factors
High-risk individuals, such as those with a genetic predisposition or previous cancer diagnoses, may benefit from more frequent or specialized screenings.
What to Remember About Cancer Screening in Singapore
Cancer screening in Singapore is widely accessible, with government initiatives promoting affordable and convenient options. Healthier SG and other national programs encourage regular screenings for early detection. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate screenings based on your health status.
Stay Updated on Guidelines
Screening recommendations can change based on new research. Regular consultations with your doctor ensure you stay informed about the latest guidelines.
Follow Up on Abnormal Results
An abnormal result doesn’t always indicate cancer but requires follow-up tests or monitoring. Prompt follow-ups can help clarify the results and take necessary action.
Maintain a Regular Schedule
Consistency is key to effective cancer screening. Adhering to recommended schedules allows for continuous monitoring and reduces the risk of late-stage detection.
How to Know Which Cancer Screening Is Right for You
Selecting the appropriate screening test involves assessing your overall health, medical history, and risk factors. Start with a general health check-up and discuss your concerns with your doctor. Genetic testing may also be recommended for individuals with a family history of certain cancers. Personalized screening plans ensure that the tests you undergo align with your specific needs.
Conclusion
Cancer screening in Singapore offers a proactive approach to maintaining health and well-being. With a range of tests designed to detect various cancers early, regular screenings are a vital component of preventive healthcare. Understanding the types of screenings available and how to choose the right one for you ensures that you take the necessary steps to safeguard your health.






